Electrical Formulas And Calculations
In this article you will find the essential Electrical Formulas And Calculations according to National Electrical Code (NEC) - Nfpa 70 .
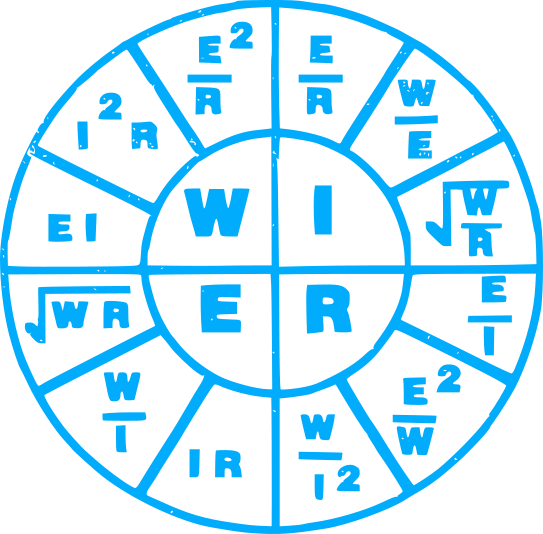
POWER
746w = 1 hp output work
E x I = Watt (true Power)
E x I = Volt-Amp (apparent power)
E x I x 1.732 = 3 Ø volt-amps
POWER FACTOR (PF)
PF = W/VA (watts divided by volt-amps)
Unity = 1.0
EFFICIENCY
EFF = Output / Input
INPUT = Output / Eff
OUTPUT = Input x Eff
OUTPUT is the work (hp) secondary
INPUT is the primary
COST
\(COST ={ { Watts * Hours Used * Rate per Hour } \over 1000}\)
Rate of March 2023 $ per kwh | september 2022 $ per kwh | |
| Denmark | $0.53 | $0.58 |
| Germany | $0.52 | $0.56 |
| United Kingdom | $0.47 | $0.42 |
| Austria | $0.46 | $0.50 |
| Italy | $0.46 | $0.58 |
| Belgium | $0.44 | $0.52 |
| Bermuda | $0.40 | $0.46 |
| Spain | $0.37 | $0.37 |
| Cayman Islands | $0.37 | $0.44 |
| Czech Republic | $0.37 | $0.45 |
| Lithuania | $0.36 | $0.50 |
| Netherlands | $0.34 | $0.49 |
| Ireland | $0.33 | $0.43 |
| Jamaica | $0.33 | $0.33 |
| Barbados | $0.33 | $0.27 |
| Estonia | $0.32 | $0.39 |
| Cape Verde | $0.30 | $0.31 |
| Latvia | $0.30 | $0.32 |
| Sweden | $0.29 | $0.35 |
| Liechtenstein | $0.27 | $0.29 |
| Guatemala | $0.27 | $0.28 |
| Cyprus | $0.27 | $0.38 |
| Slovenia | $0.27 | $0.29 |
| Portugal | $0.27 | $0.29 |
| Bahamas | $0.26 | $0.26 |
| Japan | $0.25 | $0.25 |
| El Salvador | $0.24 | $0.24 |
| Uruguay | $0.24 | $0.25 |
| Luxembourg | $0.24 | $0.24 |
| Rwanda | $0.24 | $0.22 |
| Finland | $0.24 | $0.46 |
| Honduras | $0.23 | $0.23 |
| Switzerland | $0.23 | $0.23 |
| Peru | $0.23 | $0.24 |
| Singapore | $0.22 | $0.24 |
| Belize | $0.22 | $0.22 |
| Australia | $0.22 | $0.24 |
| France | $0.21 | $0.22 |
| Mali | $0.21 | $0.22 |
| Burkina Faso | $0.20 | $0.21 |
| Slovakia | $0.20 | $0.21 |
| Gabon | $0.20 | $0.20 |
| Greece | $0.20 | $0.27 |
| Brazil | $0.20 | $0.17 |
| New Zealand | $0.19 | $0.19 |
| Togo | $0.19 | $0.19 |
| Aruba | $0.19 | $0.18 |
| Philippines | $0.18 | $0.18 |
| Poland | $0.18 | $0.19 |
| Panama | $0.18 | $0.18 |
| United States | $0.18 | $0.18 |
| Venezuela | $0.17 | $0.04 |
| Chile | $0.17 | $0.19 |
| Nicaragua | $0.17 | $0.17 |
| Kenya | $0.17 | $0.16 |
| Romania | $0.17 | $0.18 |
| Senegal | $0.17 | $0.17 |
| Uganda | $0.16 | $0.16 |
| Hong Kong | $0.16 | $0.17 |
| Costa Rica | $0.16 | $0.16 |
| South Africa | $0.15 | $0.15 |
| Macau | $0.15 | $0.16 |
| Cambodia | $0.15 | $0.15 |
| Maldives | $0.14 | $0.15 |
| Malta | $0.14 | $0.15 |
| Colombia | $0.14 | $0.17 |
| Iceland | $0.14 | $0.15 |
| Madagascar | $0.14 | $0.13 |
| Namibia | $0.14 | $0.11 |
| Norway | $0.13 | $0.13 |
| Mauritius | $0.13 | $0.13 |
| Bulgaria | $0.13 | $0.14 |
| Mozambique | $0.13 | $0.13 |
| Dominican Republic | $0.12 | $0.12 |
| Ivory Coast | $0.12 | $0.12 |
| Moldova | $0.12 | $0.15 |
| Morocco | $0.11 | $0.12 |
| Thailand | $0.11 | $0.12 |
| Canada | $0.11 | $0.12 |
| Malawi | $0.11 | $0.11 |
| Hungary | $0.11 | $0.12 |
| Albania | $0.11 | $0.12 |
| Armenia | $0.10 | $0.10 |
| North Macedonia | $0.10 | $0.12 |
| Jordan | $0.10 | $0.09 |
| Tanzania | $0.10 | $0.10 |
| Mexico | $0.10 | $0.10 |
| Ecuador | $0.10 | $0.10 |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | $0.10 | $0.10 |
| Indonesia | $0.10 | $0.10 |
| Botswana | $0.10 | $0.10 |
| Eswatini | $0.10 | $0.10 |
| South Korea | $0.09 | $0.10 |
| Taiwan | $0.09 | $0.10 |
| Belarus | $0.09 | $0.09 |
| Serbia | $0.09 | $0.10 |
| Lesotho | $0.09 | $0.09 |
| Sierra Leone | $0.08 | $0.08 |
| DR Congo | $0.08 | $0.07 |
| Cameroon | $0.08 | $0.08 |
| United Arab Emirates | $0.08 | $0.08 |
| China | $0.08 | $0.08 |
| Vietnam | $0.08 | $0.08 |
| Turkey | $0.08 | $0.07 |
| Georgia | $0.08 | $0.08 |
| India | $0.07 | $0.07 |
| Tunisia | $0.07 | $0.07 |
| Russia | $0.06 | $0.06 |
| Paraguay | $0.06 | $0.06 |
| Bangladesh | $0.05 | $0.05 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | $0.05 | $0.05 |
| Nigeria | $0.05 | $0.03 |
| Malaysia | $0.05 | $0.05 |
| Saudi Arabia | $0.05 | $0.05 |
| Bahrain | $0.05 | $0.05 |
| Azerbaijan | $0.05 | $0.05 |
| Kazakhstan | $0.05 | $0.04 |
| Nepal | $0.04 | $0.04 |
| Afghanistan | $0.04 | $0.04 |
| Sri Lanka | $0.04 | $0.05 |
| Algeria | $0.04 | $0.04 |
| Ukraine | $0.04 | $0.04 |
| Pakistan | $0.04 | $0.05 |
| Laos | $0.04 | $0.03 |
| Argentina | $0.03 | $0.03 |
| Qatar | $0.03 | $0.03 |
| Cuba | $0.03 | $0.03 |
| Myanmar | $0.03 | $0.03 |
| Ghana | $0.03 | $0.03 |
| Kuwait | $0.03 | $0.03 |
| Zambia | $0.03 | $0.03 |
| Egypt | $0.03 | $0.03 |
| Uzbekistan | $0.03 | $0.03 |
| Oman | $0.03 | $0.03 |
| Angola | $0.02 | $0.02 |
| Bhutan | $0.02 | $0.02 |
| Syria | $0.01 | $0.01 |
| Iraq | $0.01 | $0.01 |
| Kyrgyzstan | $0.01 | $0.01 |
| Suriname | $0.01 | $0.02 |
| Sudan | $0.01 | $0.01 |
| Ethiopia | $0.01 | $0.01 |
| Iran | $0.01 | $0 |
| Zimbabwe | $0.01 | $0.01 |
| Libya | $0 | $0.01 |
REQUIRED WIRE SIZE FOR AMBIANT TEMPERATURE
Load / Correction Factor or Load / Correction Factor x T.310-15b2a
T.310-15b2a : Table 310.15(B)(2)(a) Adjustment Factors for More Than Three Current-Carrying Conductors
in a Raceway or Cable
Number of Current-Carrying Conductors Percent of Values in Tables 310.16 through 310.19 as
Adjusted for Ambient Temperature if Necessary4–6
7–9
10–20
21–30
31–40
41 and above 35
80
70
50
45
40
35
(b) More Than One Conduit, Tube, or Raceway. Spacing between conduits, tubing, or raceways shall be maintained.Spacing is normally maintained between individual conduits in groups of conduit runs from junction box to junction box because of the need to separate the conduits where they enter the junction box, to allow room for locknuts and bushings. Field experience has indicated that this degree of spacing between runs has not caused any problems.
(c) Conduits Exposed to Sunlight on Rooftops. Where conductors or cables are installed in conduits exposed to direct sunlight on or above rooftops, the adjustments shown in Table 310.15(B)(2)(c) shall be added to the outdoor temperature to determine the applicable ambient temperature for application of the correction factors in Table 310.16 and Table 310.18.
| TO FIND | DC | AC 1 Ø | AC 3 Ø |
| Amperes when hp is known | \({hp * 746}\over E*Eff\) | \({hp * 746}\over E*Eff*PF\) | \({hp * 746}\over 1.732*E*Eff*PF\) |
| Amperes when kw is known | \({kw * 1000}\over E\) | \({kw * 1000}\over E*PF\) | \({kw * 1000}\over 1.732*E*PF\) |
| Amperes when kwa is known | \({kva * 1000}\over E\) | \({kva*1000}\over E*1.732\) | |
| Kilowatts | \({E*I}\over 1000\) | \({E*I*PF}\over 1000\) | \({E*I*PF*1.732}\over 1000\) |
| KVA | \({E*I}\over1000\) | \({E*I*1.732}\over 1000\) | |
| Horsepower | \({E*I*Eff}\over 746\) | \({E*I*Eff*PF}\over 746\) | \({E*I*Eff*1.732}\over 746\) |
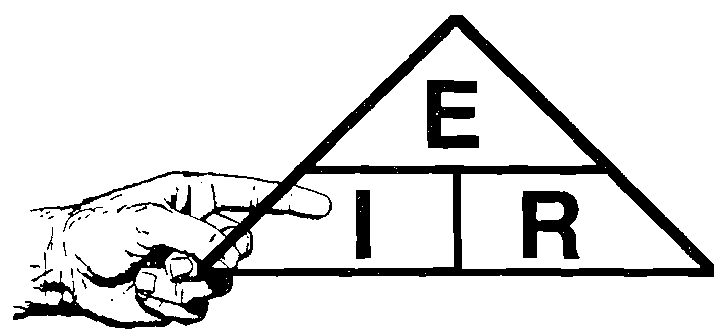
Finger Method
To solve anunknown you will need to know two knowns.
Put your finger on the one you want to solve and the other two knowns will show you how to solve it.
- To find AMPS I=E/R
- To find Volts E=I*R
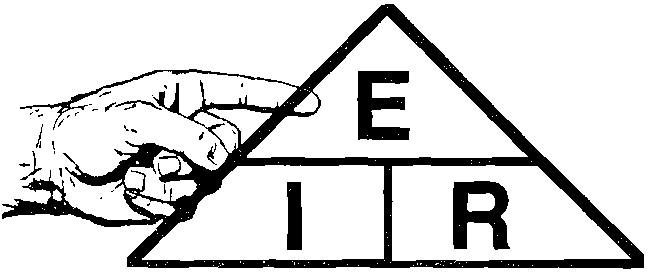
- To find Resitance R=I/R
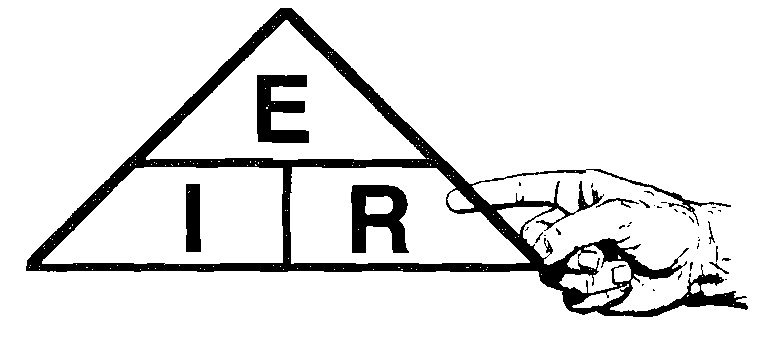
- To find Voltage E=W/I
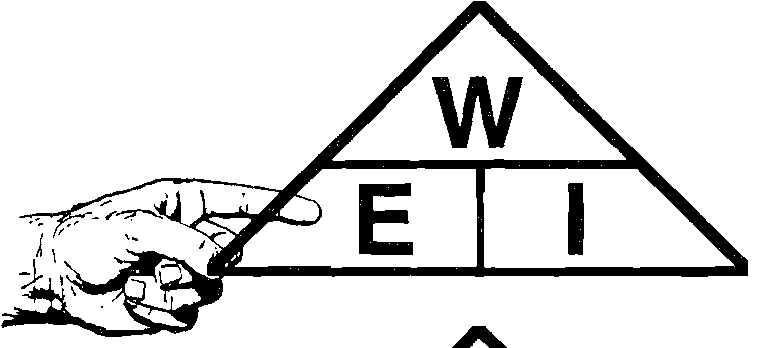
- To find Wattage W=E*I
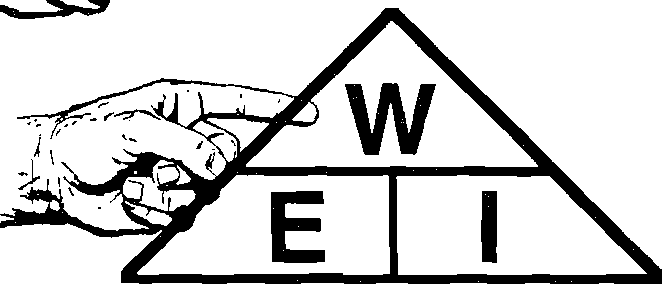
- To find Amperage I=W/E
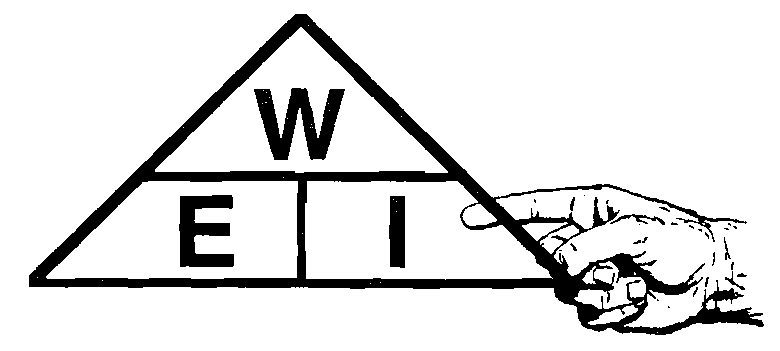
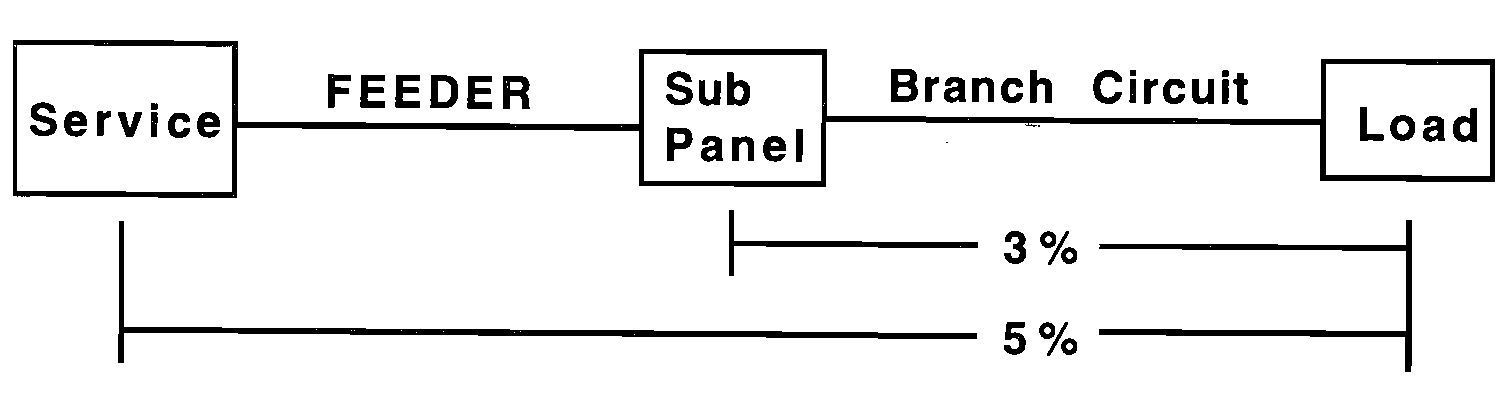
Voltage Drop
- Power Loss = VD * I
- Voltage Drop \(VD= {2*{K*D*I} \over CM}\) or VD = I*R
- Wire Size \(CM= {2*{K*D*I} \over VD per}\)
- Distance \(D={ {CM*VDper} \over 2*K*I}\)
The "2" in the formulas is for 1 Ø (one phase)
For 3 Ø change "2" to 1.732
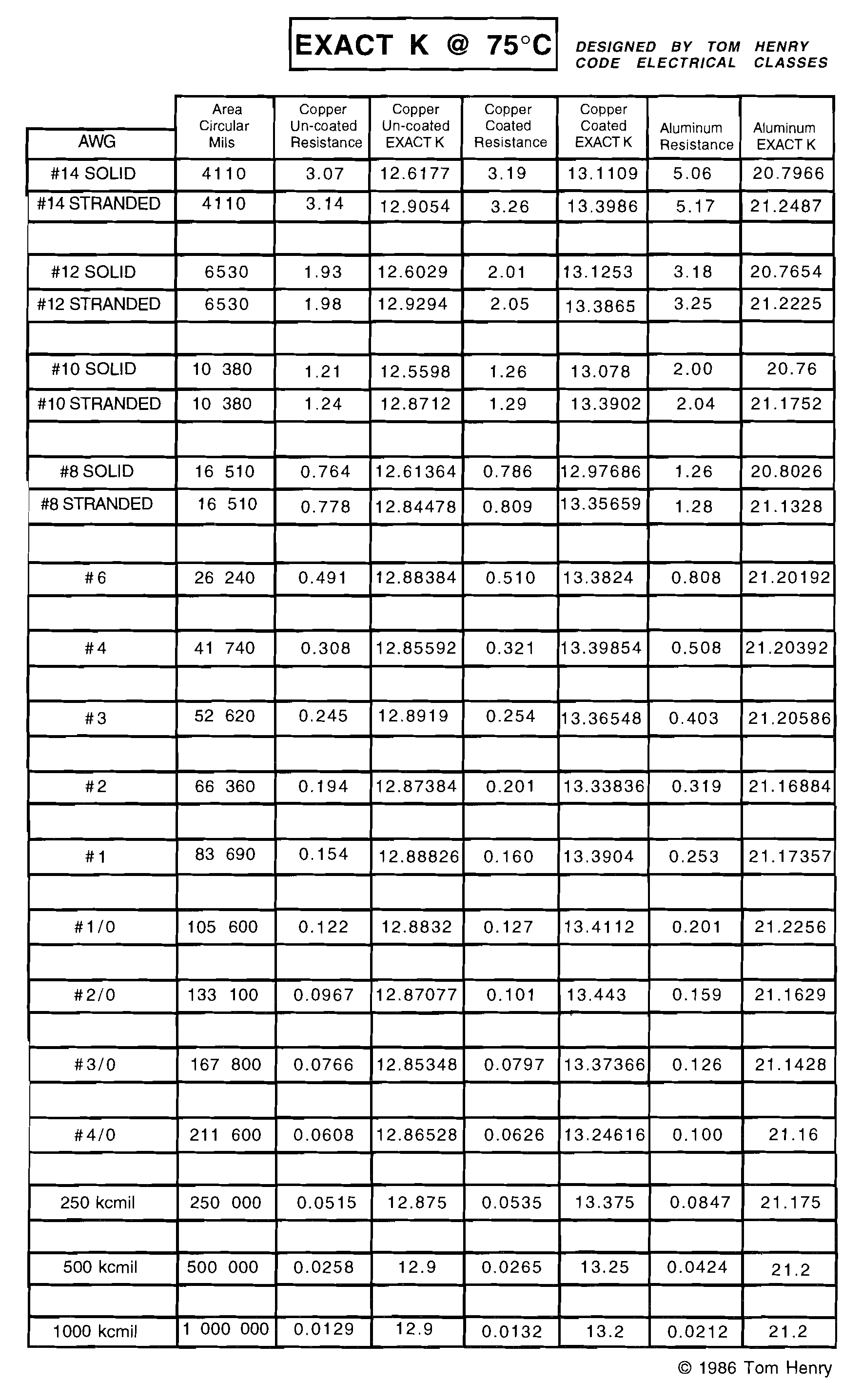
K is the resistance of a cm foot \(K = {{R*CM} \over 1000}\)
When using the formula to find Wire Size use approximate K of 12.9 for copper and 21.2 for aluminium
D is the distance On Way in a circuit
I is the load in amperes
CM is the wir size in circular mils, Foun in table below
VD per is the percentage of applied voltage : 3% VD per for branch circuit and 5% total system.
Example :
A 120 v brach circuit is permitted to drop 3% * 120v = 3.6 volts.
A 240 v branch circuit 3% * 240v = 7.2 volts.
Total system 240v * 5% = 12 volts permitted
Motor Formula
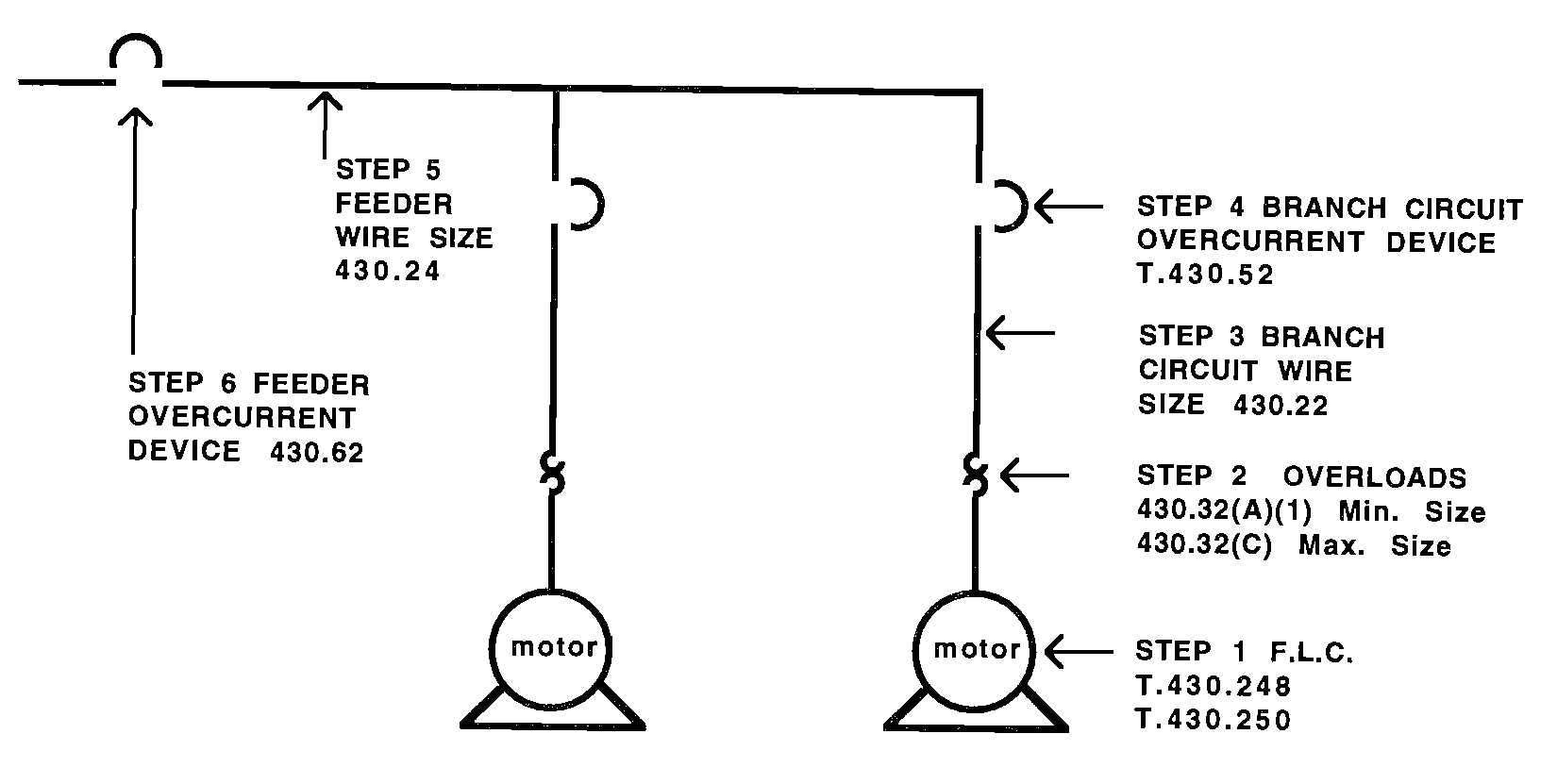
- STEP 1 F.L.C (full load current) T.430.248 1Ø and T430.250 3Ø
- STEP 2 Motor running overload protection. Thermal protector "heater"
- 430.32(A)(1) Minimum size
- 430.32(C) Maximum size
- Use motor nameplate only for heaters, if given.
- STEP 3 Branch circuit wire size 430.22 F.L.C * 125% = Required ampicity
- Table 310.16 size wire ampicity to insulation
- STEP 4 Branch circuit overcurrent protection (fuse or CB) shall be selected from Table 430.52. First select the type of motor (1Ø, 3Ø, AC, DC, wound rotor, code letter) next select type of protection (non-time delay, dual element, inverse-time, CB) the select the percentage from proper colum an multiply it times the F.L.C of motor. Use 240.6 to select the standard size the Code permits. When value found does not match a standard size,, the Code permits the next higher standard size per 430.52 ex.1.
- STEP 5 Feeder conductor size 430.24 Multiply largest rated motor in F.L.C by 128% and add the F.L.C of all the other motors connected to the same feeder conductor for required ampacity T.310.16
- STEP 6 Feeder overcurrent protection 430.62 Select the largest brach circuit over-current device and add all the other motors F.L.C connected on the same feeder to select feeder fuse or CB. The Code doas not permit going up to the next size on a feeder, must go down.
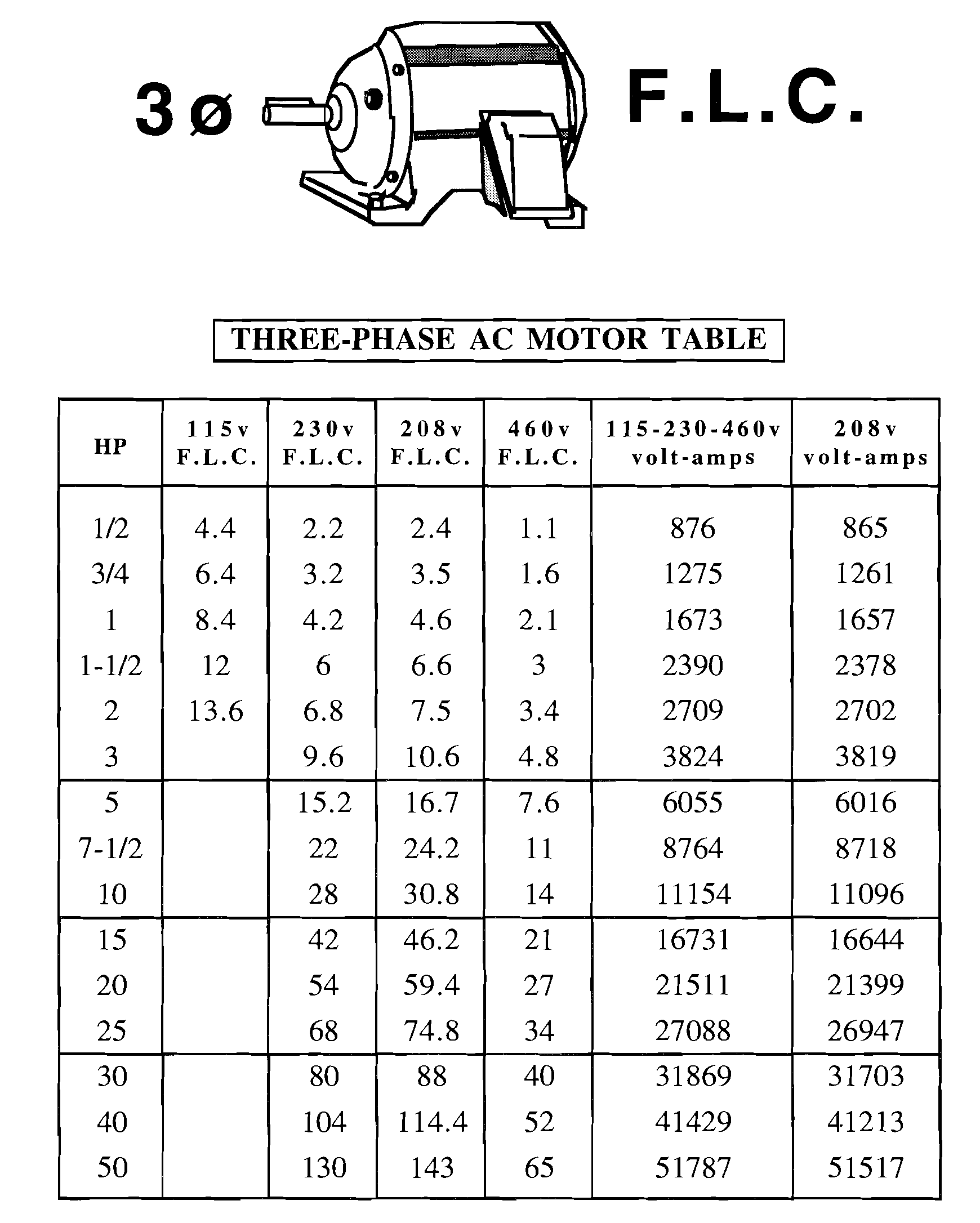
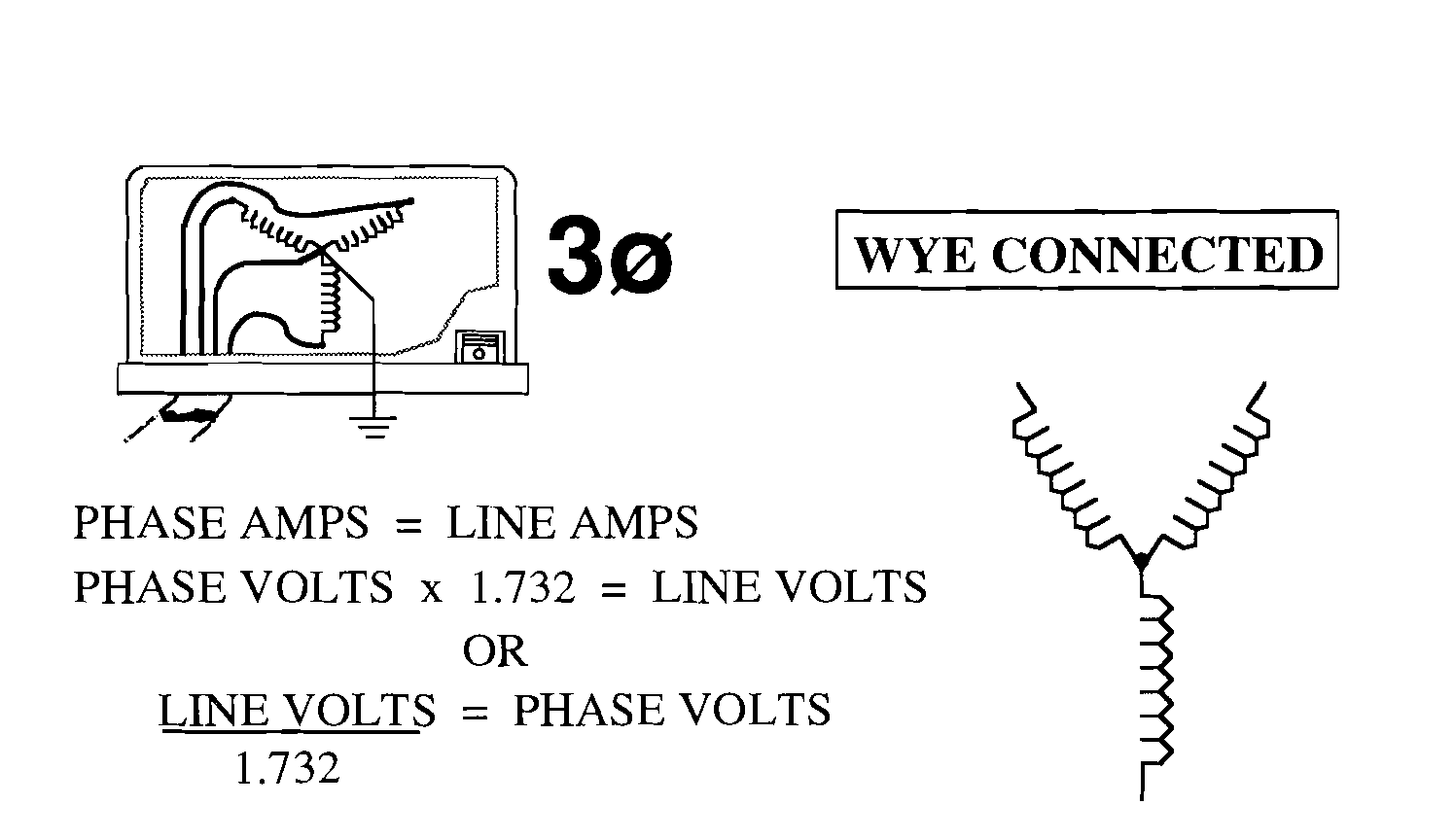
Three phase volt-amps = E * I * 1.732
Example : to calculate va input for three phase 10 HP 208v motor
208v * 30.8 amps * 1.732 = 11096 va
3Ø va = E * I * 1.732
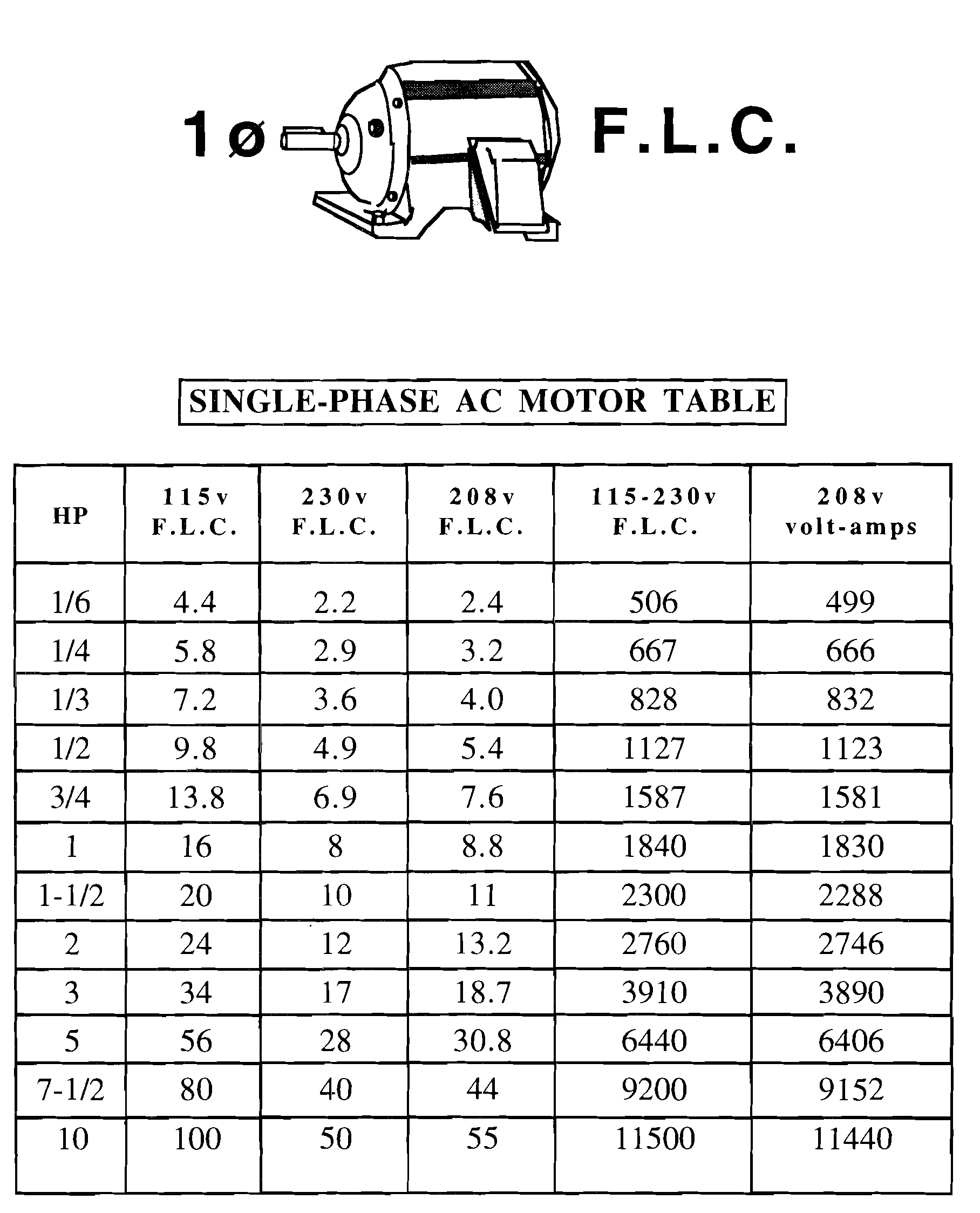
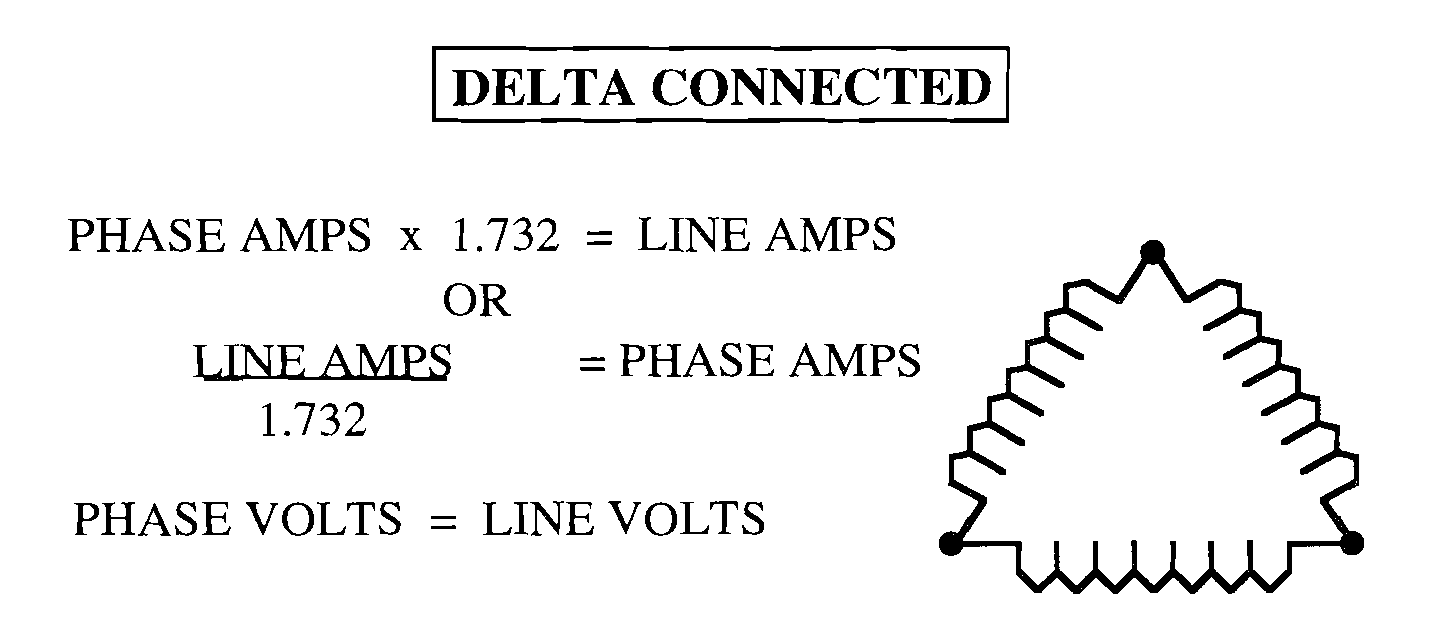
Single phase volt-amps = E * I
Example : to calculate va input for single phase 5 HP 208v motor
208v * 30.8 amps * 1.732 = 6406 va
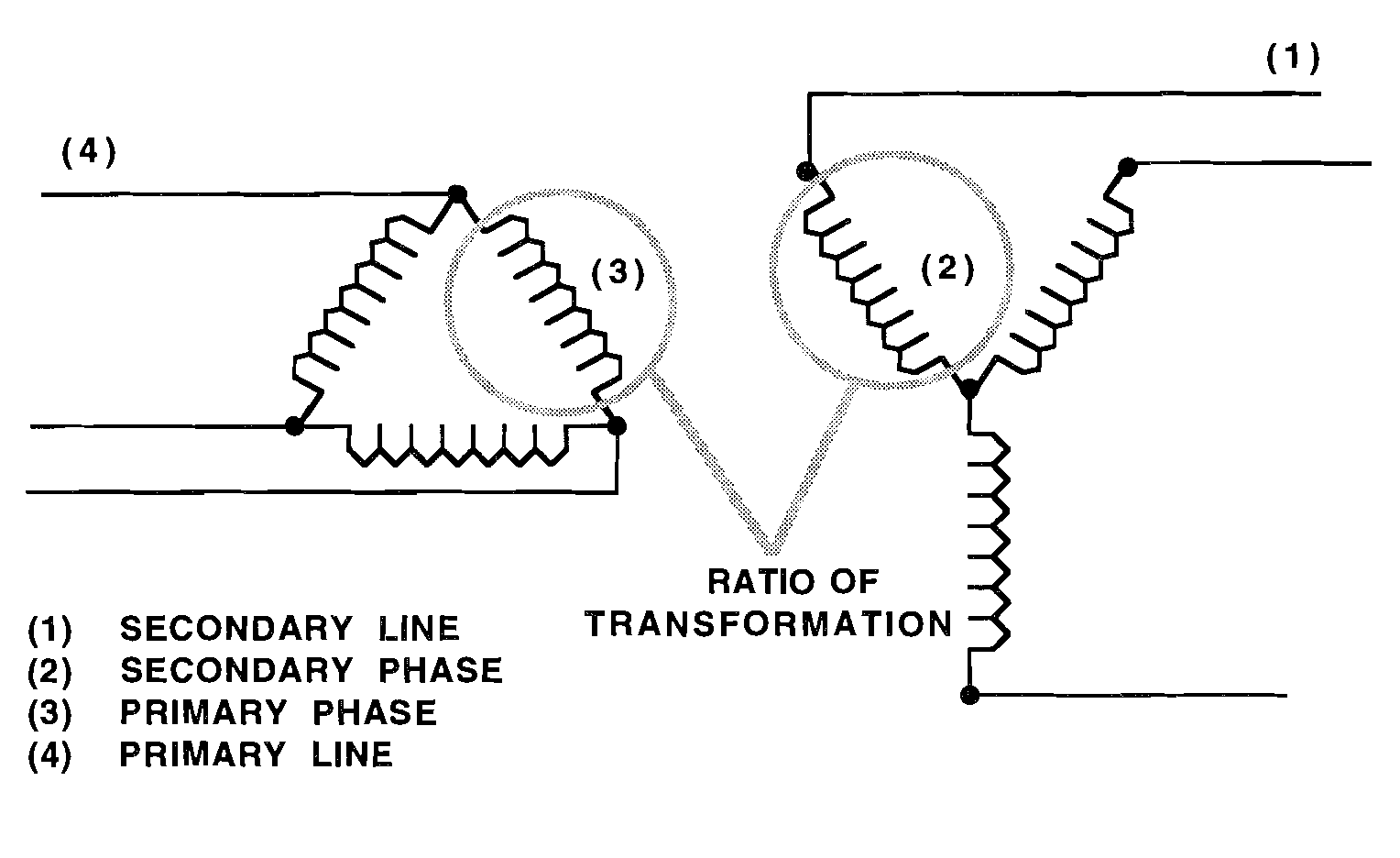
Single Phase Transformer
EP = primary voltage
Ip = current in primary
Es = Secondary voltage
Is = current in secondary
To find primary voltage wheb the current & secondary voltage are known : \(Ep ={ {Es * Is} \over Ip}\)
To find primary current when the secondary currents are known : \(Ip ={ {Es * Is} \over Ep}\)
To find secondary current when the voltages & primary current are known : \(Is ={ {Ep * Ip} \over Es}\)
Kimo
on 13 décembre 2023 at 11:51Simple et efficace Merci pour le partage